proximitySensors <<
Previous Next >> proximitySensorPropertiesDialog
proximitySensorDescription
|

Proximity sensor types and mode of operation
Proximity sensors come in 6 different types and can be customized to a large extent:
Ray-type: the ray-type proximity sensor is ideally suited for very simple modeling of a proximity sensor, or for modeling of a laser range finder. They are the fastest proximity sensors.
Randomized ray-type: the randomized ray-type proximity sensor operates as a ray-type sensor that randomly sweeps a cone volume. It has a similar appearance as the cone-type proximity sensor.
Pyramid-type: the pyramid-type proximity sensor is ideally suited for simple modeling of a proximity sensor with a detection volume that is rectangular. They are very fast.
Cylinder-type: the cylinder-type proximity sensor is ideally suited for simple modeling of a proximity sensor with a detection volume that is revolute. They are very fast.
Disk-type: the disk-type proximity sensor allows precisely modeling of a proximity sensor with a revolute-scanning detection volume. Depending on the selected precision and operation mode, they can be a little bit more calculation intensive.
Cone-type: the cone-type proximity sensor allows for the best and most precise modeling of most proximity sensors. Depending on the selected precision and operation mode, they can be a little bit more calculation intensive.
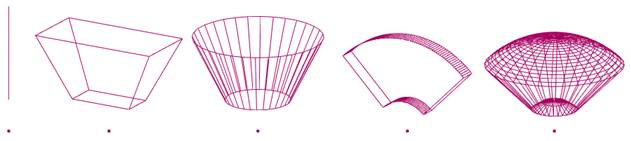
[Ray-type, pyramid-type, cylinder-type, disk-type and cone- or randomized ray-type proximity sensors]
Proximity sensors operate in a geometrically exact manner: they perform an exact distance calculation between their sensing point (small sphere) and any detectable entity that interferes with its detection volume (they don't perform a simple collision detection between the sensing volume edges like most other simulation software, but an exact distance calculation within the detection volume). Each proximity sensor will compute following minimum distance:
Sensing point <-- --> (detectable entity ∩ detection volume)
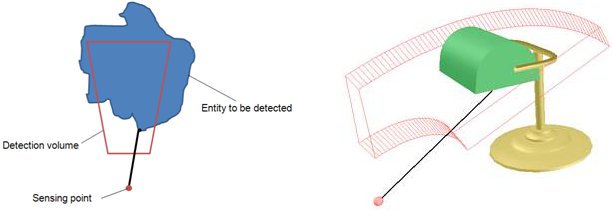
[Minimum distance calculation between sensing point and (detectable entity ∩ detection volume)]
If a proximity sensor detects an object, then a trigger is activated, which will result in a call to the trigger callback function.
|
proximitySensors <<
Previous Next >> proximitySensorPropertiesDialog